Keeping Diabetes in Check – Know Your Blood Sugar Numbers For All Diabetics
 One goal of diabetes treatment is to get your blood sugar under control. Actually that is the foremost goal. When your blood sugar stays at manageable levels, then complications are are less of an issue. But, it takes time, as well as carefully following your doctor’s instructions to find the balance. One tool that doctors use is your A1C number.
One goal of diabetes treatment is to get your blood sugar under control. Actually that is the foremost goal. When your blood sugar stays at manageable levels, then complications are are less of an issue. But, it takes time, as well as carefully following your doctor’s instructions to find the balance. One tool that doctors use is your A1C number.
Taking control of your diabetes can help you feel better and stay healthy. Keeping blood sugar close to normal reduces your chances of having heart, eye, kidney and nerve problems that can be caused by diabetes. To control your diabetes, you need to know your blood glucose numbers and your target goals.
What the A1C number means?
 You might have heard this mentioned on commercials but weren’t sure how it correlated to diabetes. Here’s a simple explanation. A glucose meter is used to determine your blood glucose level at any point throughout your day. This is important for treatment because these numbers can teach you where your diet is lacking when it comes to eating too many carbohydrates.
You might have heard this mentioned on commercials but weren’t sure how it correlated to diabetes. Here’s a simple explanation. A glucose meter is used to determine your blood glucose level at any point throughout your day. This is important for treatment because these numbers can teach you where your diet is lacking when it comes to eating too many carbohydrates.
When you are first learning to live with diabetes, it can be both frightening and confusing. You don’t realize how important the relationship is between glucose and insulin until your body can’t perform the job properly anymore. If you have been diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes, the body never developed the process to do what it is supposed to do to the glucose. You have to provide the tool since your body doesn’t automatically know what to do.
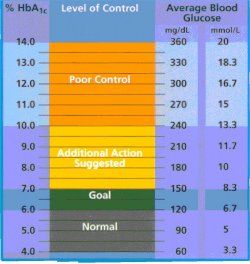 The A1C number gives a broader picture of your diabetes management for a few months at a glance. You might show good control of your diabetes this week, but still appear to have symptoms. You can test your blood sugar at any given moment and get a number that shows compliance but that may not have been the case all the time. This is where the additional testing is vital.
The A1C number gives a broader picture of your diabetes management for a few months at a glance. You might show good control of your diabetes this week, but still appear to have symptoms. You can test your blood sugar at any given moment and get a number that shows compliance but that may not have been the case all the time. This is where the additional testing is vital.
A1C is actually written HbA1C, read “glycated hemoglobin A1C.” Glucose is not the only thing swimming through the bloodstream. There are red blood cells, which gives blood its red color. These cells contain a protein called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin binds to iron in the blood.
Well, hemoglobin can also be bound by glucose. Remember it is sugar so it is sticky. Glucose that has been circulating for a while unused will bind to hemoglobin in the red blood cells. Since red blood cells live for about three months before they die, that sugar can stay bound for a good amount of time.
A1C Numbers
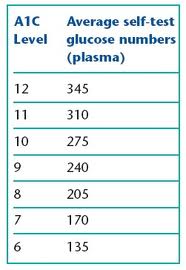 The A1C test finds those hemoglobin molecules in the red blood cells and quantifies them. The percentage of glycated (bound) hemoglobin lets the doctor know the average blood sugar over that period of time. An average glucose number is about 150mg/dl. This equals roughly seven percent on the A1C test. A percentage of eight or nine means your blood sugar has, at some point, been out of control. The test is done about four times a year.
The A1C test finds those hemoglobin molecules in the red blood cells and quantifies them. The percentage of glycated (bound) hemoglobin lets the doctor know the average blood sugar over that period of time. An average glucose number is about 150mg/dl. This equals roughly seven percent on the A1C test. A percentage of eight or nine means your blood sugar has, at some point, been out of control. The test is done about four times a year.
Your doctor will use these numbers as a guide. He or she can verify blood sugar management against your glucose monitoring logs. This is not to catch you off guard but to help you better keep your diabetes under control so you don’t run into trouble in the rest of your body systems.
Keep monitoring your blood sugar using your glucose meter, but do follow up with your doctor on a routine basis for this other very important test. The more information you gather regarding your diabetes, the more likely you will maintain control and avoid complications.
